How to Treat Chronic Ear Infections
Chronic ear infections can be frustrating and painful, particularly for those who experience them frequently. While occasional ear infections are common, chronic infections are persistent or recurrent, requiring ongoing attention and treatment. Addressing chronic ear infections effectively involves understanding their causes, recognizing symptoms, and exploring appropriate treatment options. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you manage and treat chronic ear infections.

Below, our ENT providers give some helpful tips about managing chronic ear infections for patients throughout San Diego, CA and the surrounding areas, including Burbank. Reach out to our friendly team today to learn more about our advanced sinus and allergy treatments.
What Are Chronic Ear Infections?
Chronic ear infections occur when an infection in the ear persists for an extended duration or recurs repeatedly over time. Unlike acute ear infections, which typically resolve within a few days or weeks with treatment, chronic infections can last for more than three months or occur multiple times in a short period. These infections most commonly affect the middle ear, the space behind the eardrum. Chronic ear infections may lead to fluid buildup, inflammation, and ongoing discomfort. Left untreated, they can cause complications such as hearing loss, damage to the ear structures, or even more serious infections.
What Causes Ear Infections & What Are the Risk Factors?
So, how do you get ear infections? Understanding what causes chronic ear infections can be complex, but identifying the underlying causes is key to preventing and managing them. Some of the most common causes and risk factors include:
- Inefficient Eustachian Tube Function – The eustachian tubes connect the middle ear to the back of the throat and help equalize pressure and drain fluid from the ear. If these tubes are blocked or not functioning correctly—due to inflammation, allergies, or anatomical issues—fluid can accumulate, increasing the risk of infection.
- Repeated Acute Ear Infections – Recurrent acute infections can transform into a chronic condition if left untreated or if the infections are inadequately managed.
- Underlying Medical Conditions – Nasal allergies, chronic sinusitis, or enlarged adenoids can contribute to chronic infections. Immune system deficiencies or autoimmune diseases can also make people more prone to infections.
- Environmental Factors – Exposure to secondhand smoke, frequent swimming (especially in untreated water), and poor air quality can contribute to chronic ear infections.
- Age and Anatomy Considerations – Young children are more vulnerable due to their developing immune systems and narrower, horizontally positioned eustachian tubes, which make drainage more difficult.
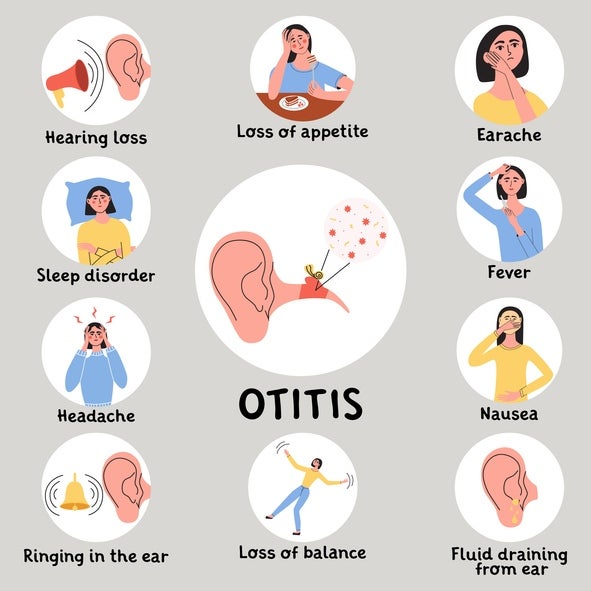
Common Signs & Ear Infection Symptoms
There are different types of ear infections. Chronic ear infections may not always present the same way as acute ear infections, making it essential to watch for key indicators. Symptoms to look out for include:
- Persistent ear pain or pressure
- Fluid drainage from the ear (may appear clear, white, or yellowish)
- Feeling of fullness or blockage in the ear
- Reduced or muffled hearing over time
- Dizziness or balance issues
- Low-grade fever in some cases
- Recurring discomfort in the ear even after treatment
If you or your child experience these symptoms repeatedly or over an extended period, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider. Identifying chronic ear infections early can help prevent potential complications like permanent hearing loss.
Treatment Options
Treating chronic ear infections typically involves a combination of medical intervention, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, surgical procedures. Here are the most common treatment options:
- Antibiotics – Antibiotics are often the first line of defense against bacterial ear infections. They may be administered orally or as ear drops, depending on the severity of the condition. However, chronic infections require careful evaluation, as excessive use of antibiotics can lead to resistance.
- Pain Relievers – Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help reduce ear pain and inflammation while treatment takes effect. Be sure to consult an ENT specialist to find out if this approach is right for you.
- Steroids – If swelling in the eustachian tubes is severe, corticosteroids may be prescribed to help bring down inflammation and improve drainage.
Ear Tubes & Surgical Interventions
For those who experience frequent or severe chronic ear infections, medical procedures may be necessary. Some of the most common procedures include the following:
- Myringotomy with Ear Tubes – This is one of the most common procedures for chronic middle ear infections. During a myringotomy, a small incision is made in the eardrum, and a tiny tube is inserted to allow fluid to drain and air to flow, which may help reduce the frequency of future infections in some individuals. The tubes typically fall out on their own after 6–12 months.
- Adenoidectomy – If enlarged adenoids contribute to chronic infections, surgical removal may reduce the frequency of infections.
- Surgery for Structural Issues – Corrective surgeries, such as repairing a perforated eardrum, may be recommended for individuals with anatomical abnormalities.
Home Remedies & Lifestyle Changes
You can do several things at home or throughout daily life to help minimize the risk of getting an ear infection, as well as easy home remedies to try. Some of those include the following:
- Warm Compress – Applying a warm compress to the affected ear can provide temporary relief for pain and improve circulation, aiding the healing process.
- Keep Ears Dry – If swimming or frequent bathing exacerbates your ear infections, consider using earplugs or drying your ears thoroughly to limit moisture buildup.
- Treat Allergies – Effective allergy treatment with antihistamines or other allergy medications can reduce inflammation in the nasal and ear passages, improving eustachian tube function.
- Avoid Irritants – Reduce exposure to secondhand smoke, pollutants, and allergens that can contribute to recurring infections.
- Strengthen Your Immune System – Focus on supporting your immune health with a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and regular exercise to help fend off infections.
Get Connected to Proven Treatments Today
Chronic ear infections are more complex than one-time ear problems but can be effectively managed with the right combination of treatments and preventive measures. Early diagnosis, appropriate medical interventions, and lifestyle changes may help reduce the frequency and severity of infections, which can support better daily comfort and long-term ear health.
If you or your child experiences persistent or recurring symptoms, don’t hesitate to consult an ear, nose, and throat specialist who can create a tailored treatment plan. Contact the team at SoCal Breathe Free Sinus & Allergy Centers San Diego if you’re ready to learn how to prevent ear infections or schedule an appointment online to get started. We’re happy to help residents throughout San Diego, CA and the surrounding areas, including Burbank.
The information provided in this article is for informational and educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. It is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease or medical condition. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment.
Results may vary: Treatment outcomes and health experiences may differ based on individual medical history, condition severity, and response to care.
Emergency Notice: If you are experiencing a medical emergency, call 911 or seek immediate medical attention.
